Spring boot3 - Spring JDBC에 대한 이해와 기본 실습
기본 JDBC를 사용하려면
Connection부터 Query 날리고, ResultSet까지 가져오는 과정이 있다.
해당 과정은 JSP/Servlet으로 톰캣서버로 웹앱 제작시 사용했었는데
Spring이 들어오고 나서
작성 부분을 조금 더 쉽게 만들 수 있도록
"JdbcTemplate"이란 녀석을 만들었다.
이번 포스팅에서는
JPA를 사용하기 전에
Spring이 제공해주는 JDBC 객체로
DB에 접근해 INSERT, DELETE를 해본다.
1. application.properties 설정
[application.properties]
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
2. resources/schema.sql 생성
[resources/schema.sql]
create table course
(
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255) not null,
author varchar(255) not null,
primary key (id)
);
insert into course (id, name, author) values (2, 'learn aws', 'in28minutes');
select * from course;
delete from course where id = 1;
3. Repository 생성
DB에 접근하는 객체는
Repository이다.
[CourseJdbcRepository.java]
package com.in28minutes_springboot.lear_jpa_andhibernate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class CourseJdbcRepository {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate springJdbcTemplate;
private static String INSERT_QUERY =
"""
insert into course (id, name, author)
values (?, ?, ?);
""";
private static String DELETE_QUERY =
"""
DELETE FROM COURSE
WHERE ID = ?
""";
public void insert(Course course) {
springJdbcTemplate.update(INSERT_QUERY, course.getId(), course.getName(), course.getAuthor());
}
public void deleteById(long id) {
springJdbcTemplate.update(DELETE_QUERY, id);
}
}
Autowired로 선언한
JdbcTemplate을 보면
springframework 패키지에서 가져왔다
따라서 context 내에 어딘가 존재하기 때문에
@Autowired 해주면 자동 삽입(DI) 된다.
4. 테스트 코드 생성
[CourseJdbcCommandLineRunner.java]
package com.in28minutes_springboot.lear_jpa_andhibernate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CourseJdbcCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner{
@Autowired
private CourseJdbcRepository courseJdbcRepository;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
Course course = new Course(3, "hello", "new Course!");
courseJdbcRepository.insert(course);
courseJdbcRepository.delete(3);
}
}
CommandLineRunner 는
코드를 바로 실행시켜주는 인터페이스고
해당 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스를 생성한다.
@Component를 선언한 이유는
@SpringBootApplication 어노테이션은
ScanComponent 어노테이션이 함께 들어있다.
ScanComponent 어노테이션은
하위에 있는 컴포넌트들을 검색해
Context로 실어준다
5. 엔티티 생성
[Course.java]
package com.in28minutes_springboot.lear_jpa_andhibernate;
public class Course {
private long id;
private String name;
private String author;
public Course() {
}
public Course(long id, String name, String author) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
}
public long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return this.author;
}
}
6. Select를 해보자
Spring JDBC가 아닌
JDBC로 조회하면
ResultSet으로 리턴을 받는다.
한 줄씩 looping 해가며
데이터를 가져왔었는데
Spring JDBC에서는
Object를 던져주면
Row에 해당하는 Column들을 Mapping 해준다고 해서
-> RowMapper 객체를 제공해준다.
위에서 작성한 두 파일을 수정하자
[CourseJdbcRepository.java]
package com.in28minutes_springboot.lear_jpa_andhibernate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class CourseJdbcRepository {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate springJdbcTemplate;
private static String INSERT_QUERY =
"""
insert into course (id, name, author)
values (?, ?, ?);
""";
private static String DELETE_QUERY =
"""
DELETE FROM COURSE
WHERE ID = ?
""";
private static String SELECT_QUERY =
"""
SELECT FROM COURSE
WHERE ID = ?
""";
public void insert(Course course) {
springJdbcTemplate.update(INSERT_QUERY, course.getId(), course.getName(), course.getAuthor());
}
public void deleteById(long id) {
springJdbcTemplate.update(DELETE_QUERY, id);
}
public Course selectById(long id) {
return
springJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
SELECT_QUERY,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Course.class),
id
);
}
}
[CourseJdbcCommandLineRunner.java]
package com.in28minutes_springboot.lear_jpa_andhibernate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CourseJdbcCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner{
@Autowired
private CourseJdbcRepository courseJdbcRepository;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
Course course = new Course(3, "hello", "new Course!");
Course course2 = new Course(5, "hello", "new Course!");
courseJdbcRepository.insert(course);
courseJdbcRepository.insert(course2);
courseJdbcRepository.deleteById(3);
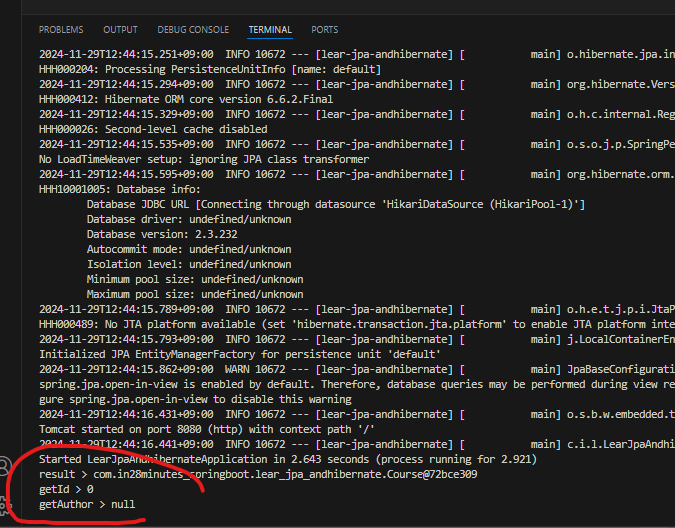
Course result = courseJdbcRepository.selectById(5);
System.out.println("result > " + result);
System.out.println("getId > " + result.getId());
System.out.println("getAuthor > " + result.getAuthor());
}
}